16. September 2016
Im Blog des Soziologie Magazins diskutieren Andreas Bischof und Vivien Sommer entlang des Lehr-Lern-Projektes »Medien und Asyl« die Arbeit von qualitativ-empirisch forschenden Soziologinnen und Soziologen, die am Rande ihrer Disziplin beschäftigt sind – etwa als Lehrende in angrenzenden Fachbereichen oder als ›Dienstleister‹ in Technik- und Entwicklungsprojekten. Die Autoren kommen dabei unter anderem zu folgendem Schluss:
Weiterlesen »
16. August 2016
Der in den Social Movement Studies erschienene Artikel »Masses, Crowds, Communities, Movements: Collective Action in the Internet Age« von Ulrich Dolata und mir ist nun bis Ende des Jahres kostenfrei bei Taylor & Francis abrufbar.
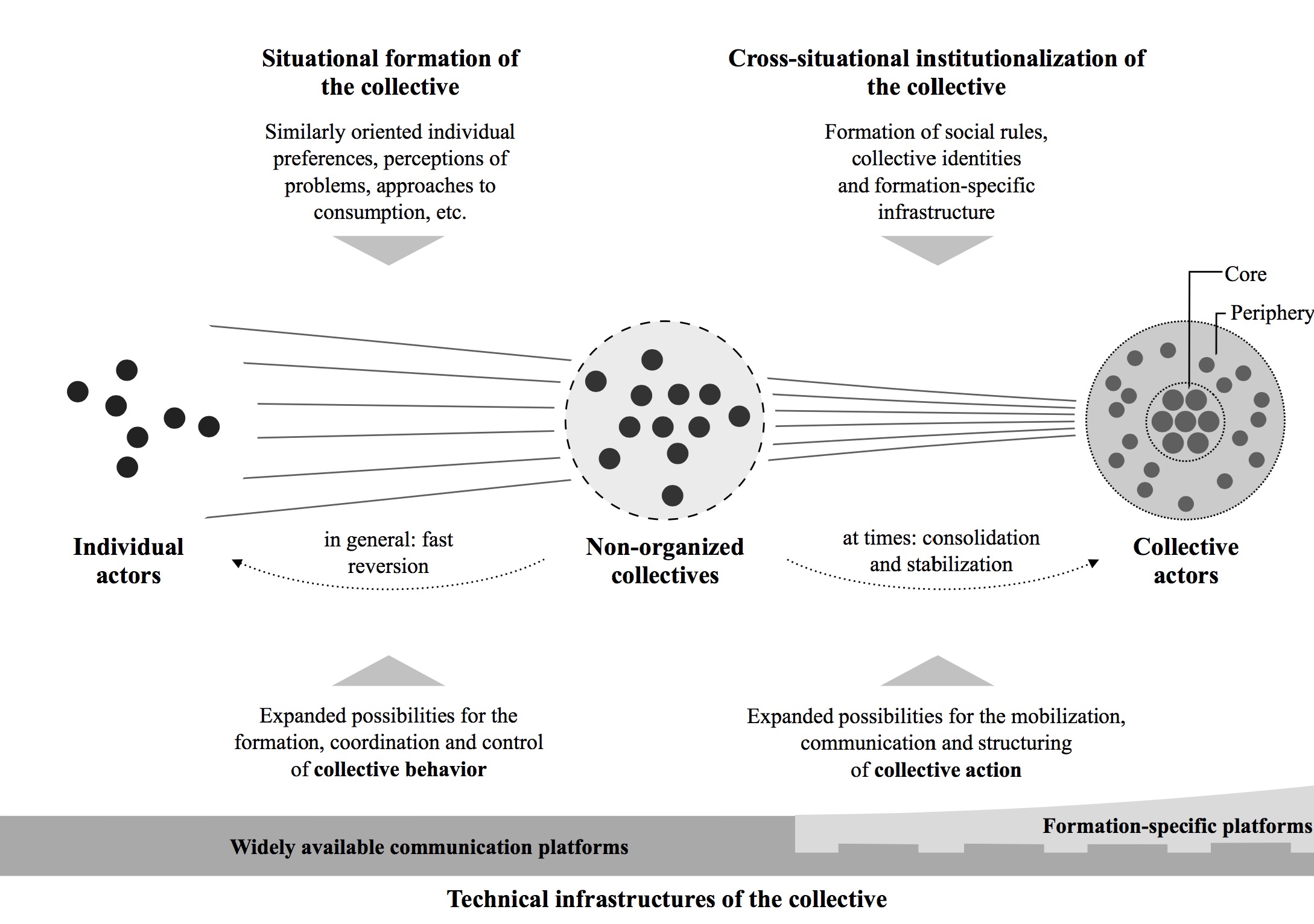
zum Artikel »
24. Juli 2016
In der Debatte (Heft 15, S. 22–25, hg. durch die Brandenburgische Akademie der Wissenschaften) ist ein kurzer Aufsatz von Renate Mayntz (*1929) erschienen, der sich mit der Ambivalenz des ›Neuen‹ in der Wissenschaft auseinandersetzt:
»[…] In der Technikentwicklung – und damit in den Technikwissenschaften – ist Können die Frucht von Innovation – ›neu‹ heißt ›besser‹, besser heißt schneller, leichter, billiger – ob es um Licht, Verkehr oder Kommunikation geht. Das Risiko ist hier, dass das Neue nicht funktioniert. Im Unterschied zu den Wirtschaftswissenschaften ist das Janusgesicht des Neuen sowohl in den Technikwissenschaften wie in den angewandten Naturwissenschaften präsent. Bei fast allen naturwissenschaftlich basierten technischen Neuerungen wurde und wird die Möglichkeit negativer Folgen gesehen.
[…] Die Frucht des Neuen in nicht unmittelbar praxisbezogenen Disziplinen ist kein Können, sondern ein Wissen. […] Neues Wissen über die Beschaffenheit der Welt zu gewinnen setzt nicht nur die Bereitschaft voraus, bislang für wahr Gehaltenes anzuzweifeln, sondern auch die Fähigkeit zu erkennen, dass etwas gar nicht Gesuchtes […] der Wirklichkeit näher kommt als das bisher Geglaubte.
Weiterlesen »
6. Juli 2016
Die Ausgabe 3/2016 der Zeitschrift Soziologie ist erschienen. In ihr findet sich (u.a. neben Peter L. Bergers Essay »Im Strudel der Flüchtlingskrise«) auch mein Beitrag »Soziologie als ›Marke‹« (Postprint):
Dieser Artikel diskutiert die Identität der Soziologie als ›Dachmarke‹ zahlreicher Forschungsfelder entlang ausgewählter Stellungsnahmen von Auguste Comte, Norbert Elias, Niklas Luhmann, Jürgen Habermas und Renate Mayntz. Dabei zeigt sich, dass die selbstgestellte Aufgabe der Soziologie seit jeher weniger in der Kommentierung tagesaktueller Ereignisse, sondern in der Beobachtung langfristiger gesellschaftlicher Entwicklungen und der Entzauberung von Beschreibungsmythen besteht. Gleichwohl kann die Soziologie auf eine disziplinübergreifende Professionalisierung ihrer Öffentlichkeitsarbeit nicht verzichten.

13. Mai 2016
Göran Ahrne (Stockholm) und Nils Brunsson (Uppsala), die bereits seit geraumer Zeit neue Organisationsformen in der digitalen Moderne in den Blick nehmen, haben jüngst zusammen mit David Seidl (Zürich) den kostenfrei abrufbaren Überblicksartikel »Resurrecting organization by going beyond organizations« veröffentlicht, in dem sie im Anschluss an James M. March und Herbert A. Simon (1958) sowie Niklas Luhmann (2000, 2005, 2012) dafür plädieren, Organisationen als rekursive Entscheidungszusammenhänge zu begreifen. Dabei identifizieren sie fünf Entscheidungstypen als Kernelemente einer voll ausgebildeten Organisation:
Weiterlesen »
12. April 2016
Inzwischen ist der Studienbrief »Kommunikation und Partizipation im Social Web. Eine Übersicht«, den ich im Jahr 2014 für die Fernuniversität in Hagen verfasst habe, als Autorenversion auch als kostenloser Download verfügbar:

»Das Internet hat als erstes ›Universalmedium der Menschheitsgeschichte‹ (Holland 1997) bereits in den 1990er Jahren eine breite sozialwissenschaftliche Debatte zu seinen soziokulturellen wie -ökonomischen Rückwirkungen angestoßen und das sogenannte ›Web 2.0‹ hat entsprechende Diskussionen ab 2005 weiter befördert.
Mit Blick auf die damit verbundenen, teilweise sehr weitreichenden Zukunftsvorstellungen die Übersicht zu behalten sowie zwischen tatsächlich gegebenen Trends und hochfliegenden Prophetien zu unterscheiden, erscheint allerdings nicht immer einfach […].
Eine kleine Navigationshilfe zur weiteren Beschäftigung mit dem gesellschaftlichen Wandel, der durch die Onlinetechnologien angestoßen worden ist, bietet dieser Studienbrief, der seinen Schwerpunkt auf die langfristigen Transformationsdynamiken legt, die aus den neuen Kommunikationsweisen im Netz resultieren. Der Band will einen kontextorientierten Überblick zum Social Web als soziotechnisches Phänomen vermitteln, das durch das Ineinanderwirken vielfältiger gesellschaftlicher sowie technologischer Einflussfaktoren geprägt ist, und führt Schritt für Schritt in die damit verbundenen Diskurszusammenhänge ein. […]«
12. März 2016
Dem derzeitigen ›4.0‹-Trend folgend hat Dirk Baecker unlängst in seinem lesens- wie diskussionswerten Essay »Oszillation 4.0« (auf dem jungen sozialwissenschaftlichen Nachrichtenportal Soziopolis) die Mediengeschichte neu aufgerollt und – wie der Titel schon sagt – entlang des Begriffs der ›Oszillation‹ in 4 Phasen gegliedert:
 Weiterlesen »
Weiterlesen »